BioByte 089: ten commandments of drug R&D, a foundation model for CGMs, expanding the genetic code without modifying the genome
Welcome to Decoding Bio’s BioByte: each week our writing collective highlight notable news—from the latest scientific papers to the latest funding rounds—and everything in between. All in one place.
If you haven’t already, please fill out this survey to help us improve Decoding Bio. It takes just a few minutes to complete. Thank you!
What we read
Why Will Healthcare be the Industry that Benefits the Most from AI? [Julie Yoo, a16z, August 2024]
Over the last few years, AI has made its way to the forefront of numerous industries, but healthcare is notably not one of them. In this article, Julie Yoo of a16z articulately explains why healthcare serves to benefit more readily than other sectors from an adoption of AI.
Within healthcare, there has historically been a slower adoption of new technology and software; however, this slower adoption presents the industry with a unique opportunity for AI integration. The relative dearth of software expenses might actually be a boon, as the sunk cost bias of prior software adoption when considering AI as a replacement is all but eliminated.
Furthermore, healthcare is currently facing one of the most severe staffing crises. “We’re short over 100,000 doctors and nurses relative to the level of (rapidly growing) demand for clinical services that is projected in the next 5 years,” a startling statistic Yoo presents. With the increasing treatment and diagnostic complexity accompanying the accelerated innovation in biotech, clinicians require greater assistance to decode vast swaths of data and deploy optimal clinical judgment. The capabilities of administrative and clinical AI products render them well-positioned to help compensate for the staffing shortage.
Healthcare constitutes a massive $4 trillion+ industry. The propensity of AI products to function as “AI staff” affords a massive opportunity to bolster this sector. With already established regulatory guidelines for AI applications in real-world clinical settings and a significant need, the timing is right for AI startups to enter and scale within this formidable space.
Phil Needleman’s Ten Commandments of Drug R&D [LifeSci VC, 2013]
Phil was the CSO of Pharmacia when it merged with Pfizer, Searle, and Monsanto. In this older post, Phil explains his ten commandments of R&D. Are these still relevant? What are your thoughts?
“There’s only one Nobel prize…” and industry researchers aren’t likely to get it.
“Phenomenology is very different than pharmacology”.
“Anything put on hold is dead”
“Define and do the Killer experiments”
“If you don’t know where you are going, all roads will get you there”.
“Make sure it’s doable in my lifetime”
“Find the shortest route to heaven”.
“I’m from Missouri… show me data”.
“Mechanisms should become lifecycle management platforms”.
“The world belongs to finishers”.
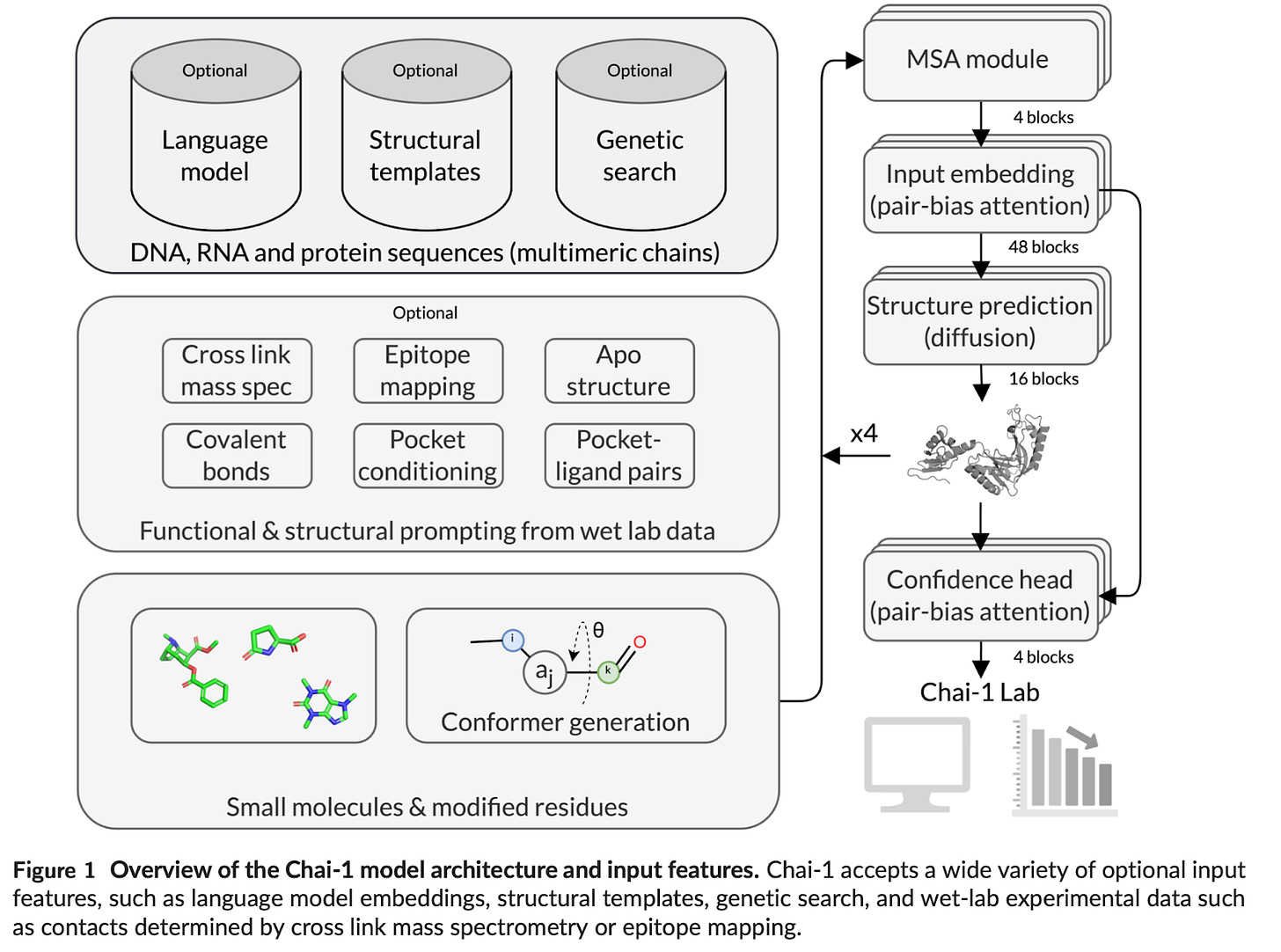
Introducing Chai-1: Decoding the molecular interactions of life [Chai Discovery, Sep 2024]
A new startup Chai Discovery just launched with $30M in seed funding from Thrive, OpenAI, Dimension, and others also published this week a white paper on Chai-1, their first multi-modal foundation model for molecular structure prediction. The model architecture was based on AlphaFold-3, with a couple modifications:
Language model embeddings: Chai-1 is trained on a combination of multiple sequence alignments (MSAs) and protein language model embeddings generated by a 3 billion parameter model. This allows for per-residue embeddings for each input protein sequence, and broader applicability to proteins that do not have sufficient evolutionary information from MSAs.
Constraints features: The model incorporates new training features designed to mimic experimental constraints common in drug discovery, such as pocket, contact, and docking constraints. During inference, the model can be prompted with constraints such as constraints around complex interactions between different parts of a molecular structure as measured by mass spec.
Chai-1 achieved several significant results across various biomolecular structure prediction tasks, with particular strengths in multimeric complex predictions and incorporating experimental constraints. Its ability to perform well in single-sequence mode without MSAs is also a notable advancement. Some highlights:
Chai-1 achieved a 77% success rate on the PoseBusters benchmark set, comparable to AlphaFold3's 76%.
Chai-1 outperformed AlphaFold Multimer 2.3 (AF2.3) on a low-homology evaluation set, with an average success rate of 75.1% compared to 67.7% for AF2.3, highlighting the value of single residue language embeddings that reduce reliance on MSAs.
Chai-1 significantly outperformed AF2.3 on antibody-protein interfaces.
Adding experimental constraints (e.g., epitope residues) significantly improved predictions, especially for antibody-antigen interactions.
The model is available for free via a web interface, including for commercial applications. The model weights and inference code was also released as a software library for non-commercial use.
From Glucose Patterns to Health Outcomes: A Generalizable Foundation Model for Continuous Glucose Monitor (CGM) Data Analysis [Segal et al, arXiv, 2024]
CGMs are one of the latest health-tech trends, becoming ubiquitous not only in patients with pre/diabetes but also in individuals who want to better understand how their body responds to different foods and activities such as stress. In this preprint, researchers have developed a transformer-based foundational model trained on CGM data from 10,812 non-diabetic individuals from the Human Phenotype Project. The researchers demonstrate that their model can predict aspects of metabolic health not solely restricted to traditional glycemic analysis, suggesting it has the potential to provide a picture of general health.
Relay breast cancer drug shows potential in early trial [Pagliarulo, BiopharmaDIVE, September 2024]
A great milestone for AI-first biotech, Relay Therapeutics has announced encouraging results from a small clinical trial of its experimental breast cancer drug, RLY-2608. Key findings include:
Tumor growth delay: Median progression-free survival of 9.2 months when combined with hormonal therapy.
Tumor shrinkage: Nearly 75% of patients at the target dose experienced some degree of tumor reduction.
Safety profile: Fewer high-grade side effects compared to existing PI3Ka inhibitors.
The drug targets mutated PI3Ka proteins using a novel approach that aims to reduce toxicity associated with current treatments. RLY-2608 is designed to selectively inhibit mutant PI3Ka while sparing the wild-type version.
Based on these results, Relay plans to advance the drug combination into a pivotal trial next year, comparing it to existing treatments like AstraZeneca's Truqap. The company is also exploring triplet combinations for first-line treatment.
This development has significant implications for treating HR-positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer with PI3Ka mutations, potentially offering improved efficacy and tolerability over current options, and is a compelling case study for AI in biotech.
Efficient genetic code expansion without host genome modifications [Costello et al., Nature Biotechnology, 2024]
Noncanonical amino acids (ncAAs) have been a well established substrate for expanding the genetic code; however, methods to incorporate these are challenging, low-throughput, and laborious. In this paper, the authors report on a new system for incorporating multiple ncAAs into proteins in living bacterial cells. Their key insight was that codon usage patterns surrounding quadruplet codons can significantly impact decoding efficiency. By optimizing these patterns and other circuit components, they created a platform capable of efficiently incorporating up to three different ncAAs into a single protein without necessitating host genome modifications.
The team began by investigating how local codon context affects quadruplet decoding, using fluorescence-activated cell sorting of GFP reporter libraries. They found that high-usage codons immediately downstream of quadruplet codons improved decoding efficiency. Building on this, they developed a "codon compression" strategy, recoding entire genetic circuits to use only high-usage codons for each amino acid. This eliminated off-target decoding events and improved on-target efficiency.
Next, the authors optimized various components of their genetic circuits, including plasmid construct designs, copy numbers, ribosome binding sites, and tRNA sequences. Through directed evolution experiments, they improved the activity of several quadruplet-decoding tRNAs. They also expanded the substrate scope of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (tRNA ligases that attach the appropriate amino acid onto cognate tRNA) to accept a broader range of ncAAs. In total, they created five mutually orthogonal tRNA-synthetase pairs capable of efficiently incorporating 47 different ncAAs.
To demonstrate the power of their system, the authors used it to synthesize macrocycles in E.coli. Using split-intein circular ligation, they generated libraries of macrocycles containing up to three different ncAAs. In total, they produced over 100 unique macrocycles, including 17 with three distinct ncAAs. This approach bridges the gap between in vitro and in vivo genetic code expansion methods, and will likely serve as an important tool for the discovery of novel bioactive peptides.
What we listened to
Notable Deals
Gilead and Genesis Therapeutics partner with $35M upfront. The duo will jointly discover novel therapies leveraging Genesis’ platform that uses AI to better explore molecular space. Gilead will then receive exclusive rights to develop and commercialize the resulting products.
Galy raises $33M Series B to pioneer cellular agriculture. The proceeds will be used to progress Galy’s lab-produced cotton to pre-industrial scale quantities. The round was lead by Breakthrough Energy Ventures as well as Inditex and H&M Group.
Candid Therapeutics emerges from stealth with $370M and two licensed clinical-stage T-cell engagers which is it repositioning for autoimmune diseases.
Bain Capital Life Sciences raises $3B+ for its fourth life sciences fund.















Please subscribers me